
Introduction to the Science of Learning
Have you ever wondered how your brain manages to absorb and retain information? The process seems almost magical. Yet, behind this magic lies a fascinating science that explores the intricate workings of our brains during learning. From the moment we encounter new concepts to the time we recall them later, several complex mechanisms come into play.
Understanding these processes can unlock new approaches to education and personal growth. Whether you’re a student striving for better grades or an adult seeking lifelong learning, knowing how your brain functions can significantly enhance your ability to learn effectively. So let’s dive into the captivating world of neuroscience and discover what makes our brains tick when it comes to absorbing and retaining information!

The Brain and Learning: Understanding the Connection
The brain is a remarkable organ, intricately designed to facilitate learning. Neurons communicate through electrical impulses and chemical signals, forming networks that enable us to absorb new information.
When we encounter something novel, our brains engage in a process known as neuroplasticity. This adaptability allows the creation of new pathways, reinforcing knowledge as we practice and repeat tasks.
Different areas of the brain play crucial roles in various types of learning. The hippocampus is vital for memory formation, while the prefrontal cortex aids in decision-making and problem-solving.
Emotions also impact how effectively we learn. Engaging emotions can enhance retention by making experiences more memorable. Thus, understanding this connection between our brains and learning strategies opens doors to improved educational practices and personal growth opportunities.
The Three Stages of Memory: Encoding, Storage, and Retrieval
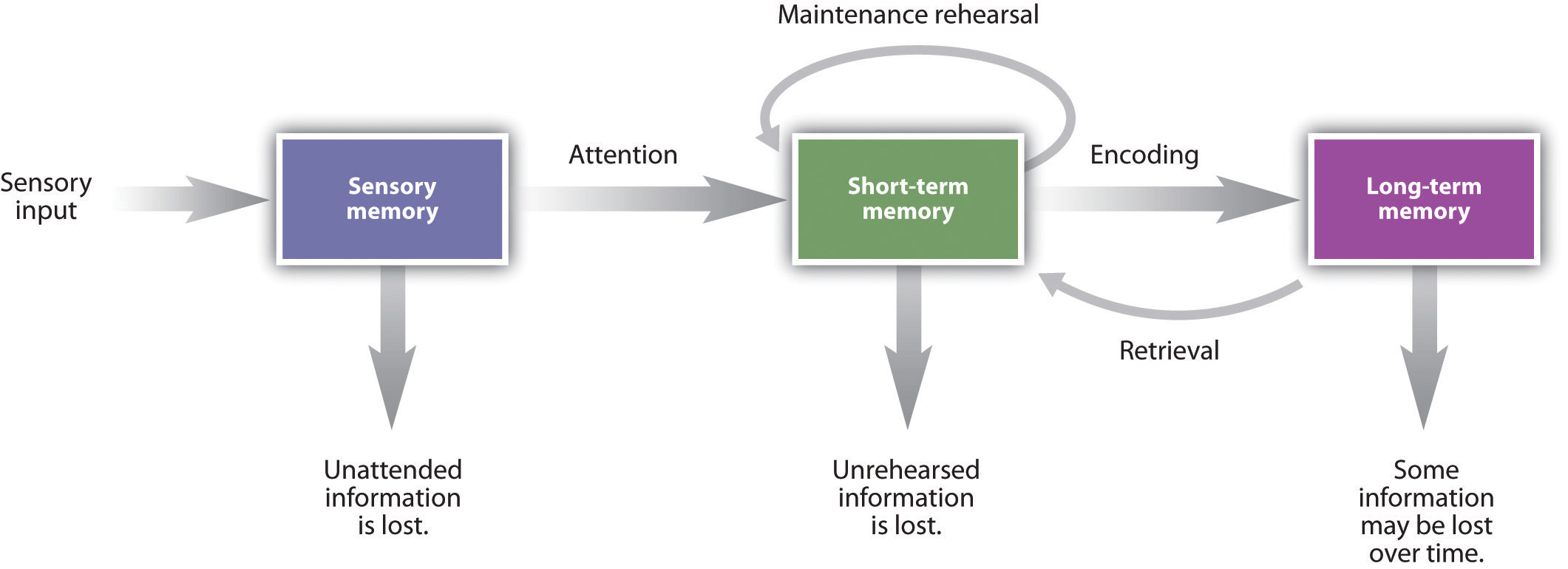
Memory operates through three essential stages: encoding, storage, and retrieval. Each stage plays a crucial role in how we learn and retain information.
Encoding is the initial step where information transforms into a format that our brains can process. This involves attention and perception, as only what we focus on can be encoded effectively.
Next comes storage. Once data is encoded, it needs to be saved for future use. Our brain houses this information in various types of memory—short-term or long-term—depending on its significance.
Retrieval is the final stage, allowing us to access stored memories when needed. The success of retrieval depends on several factors like cues and context that trigger recognition or recall.
Understanding these stages helps us grasp how our minds absorb knowledge and reinforces effective learning strategies.
Factors that Affect Learning and Memory
Learning and memory are influenced by a variety of factors. One key element is attention. When we focus our minds on specific tasks, information becomes easier to absorb.
Emotions also play a significant role. Positive feelings can enhance retention, while stress and anxiety may hinder it. A calm mind fosters better learning conditions.
Sleep is another critical factor. Adequate rest helps consolidate memories, making it easier to recall information later. Without sufficient sleep, cognitive performance declines.
Moreover, the environment matters too. A quiet space with minimal distractions allows for deeper concentration and understanding of material.
Individual differences such as age or prior knowledge impact how effectively someone learns new concepts or retains information over time. Recognizing these variables is essential in tailoring effective learning strategies.
Tips for Enhancing Learning and Memory
To enhance learning and memory, start by harnessing the power of active engagement. Instead of passively reading, try to teach the material to someone else. This helps solidify your understanding.
Another effective strategy is spaced repetition. Break study sessions into shorter intervals spread over time rather than cramming all at once. This technique allows your brain to absorb information more thoroughly.
Incorporate multiple senses into your learning process. Use visuals, auditory materials, or hands-on activities that resonate with you. The richer the experience, the better your brain retains information.
Don’t underestimate rest! Quality sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation. Ensure you’re getting enough restorative sleep each night for optimal cognitive function.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and proper nutrition. Physical well-being directly impacts mental performance and enhances overall brain health.
Applying the Science of Learning in Education
Applying the science of learning in education can transform classrooms into dynamic spaces for growth. Understanding how brains absorb and retain information is vital for educators.
Interactive teaching methods encourage students to engage actively with content. Techniques such as collaborative projects or hands-on experiments help deepen understanding and retention.
Incorporating technology also plays a significant role. Educational apps and online resources provide personalized learning experiences that cater to individual needs.
Additionally, spaced repetition enhances memory retention. By revisiting material over time, learners solidify their knowledge, making it easier to recall later.
Encouraging a growth mindset fosters resilience among students. When they view challenges as opportunities rather than obstacles, their willingness to learn increases dramatically.
Creating an environment that prioritizes emotional well-being can enhance cognitive performance. Happy learners are more likely to absorb new information effectively.

Conclusion
Understanding the science of learning reveals fascinating insights into how our brains absorb and retain information. By delving into the relationship between cognitive processes and memory, we can enhance our educational approaches.
The brain is a complex organ that thrives on connections. Learning happens through neural pathways formed during experiences. Knowing this helps us appreciate how different stimuli affect our ability to learn.
Memory operates in three stages: encoding, storage, and retrieval. Each stage plays a crucial role in how effectively we grasp new concepts and recall them later. When we know these stages, it becomes clearer why certain techniques work better for some individuals than others.
Various factors impact learning and memory retention—from emotional states to environmental influences. Recognizing these variables enables learners to create optimal conditions for study sessions.
Incorporating techniques like spaced repetition or active engagement can significantly improve one’s ability to absorb knowledge effectively. These strategies are not just useful; they’re backed by research showing their efficacy in increasing retention rates.
As educators adapt their methods based on scientific understanding, students benefit greatly from tailored teaching approaches that resonate with the brain’s natural learning processes.
Embracing the science behind learning encourages innovation in both personal study habits and classroom environments—ultimately leading to more effective ways of absorbing information long term.



Leave a Reply